Tukaj lahko najdete koristne vire, ki so nastali tekom raziskovalnega dela laboratorija.
Avtorji programske opreme so različni sodelavci laboratorija LMI. Za licenčne pogoje preverite dokumentacijo.
Programska oprema
Matlab orodja INFace v2.1

Opis v angleščini: The INFace (Illumination Normalization techniques for robust Face recognition) toolbox is a collection of Matlab functions intended for researchers working in the filed of face recognition. The toolbox was produced as a byproduct of the research work presented here. It includes implementations of several state-of-the-art photometric normalization techniques and a number of histogram manipulation functions, which can be useful for the task of illumination invariant face recognition.
Dosegljiva preko: INFace homepage, Matlab central
Documentacija: PDF
PhD zbirka orodij za razpoznavanje obrazov

Opis v angleščini: The PhD (Pretty helpful Development functions for) face recognition toolbox is a collection of Matlab functions and scripts intended to help researchers working in the filed of face recognition. The toolbox was produced as a byproduct of the research work presented here and here. It includes implementations of several state-of-the-art face recognition techniques as well as a number of demo scripts, which can be extremely useful for beginners in the field of face recognition.
Dosegljiva preko: PhD toolbox homepage, Matlab central
Documentacija: PDF
Lokalizacija karakterističnih obraznih točk
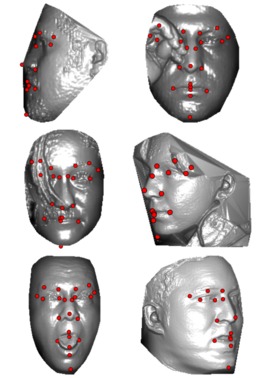
Implementacija lokalizacije karakterističnih obraznih točk iz 3D slik obrazov, ki je robustna na moteče dejavnike, kot je spremenljiva orientacija obrazov na slikah. Udejanjeni lokaliztor točk združi več linearnih kaskadnih regresijskih modelov, kjer je posamezen model naučen za omejen obseg orientacij, v en sam model, ki je zmožen lokalizirati točke na poljubno orientiranem obrazu. Razvili smo dva različna pristopa: i) prvi uporablja mehanizem večkratnega gradientnega spusta v povezavi z uveljavljenimi (ročno izdelanimi) funkcijami HOG za poravnavo obraza; ii) drugi se hkrati nauči smeri gradientnega spusta kot tudi binarne značilke, ki so optimirane za naloge lokalizacije točk in poleg konkurenčnih rezultatov zagotavljajo tudi izjemno hitro obdelavo.
Dosegljivo preko: BitBucket
Dokumentacija: PDF
Zbirke podatkov
Podatkovna zbirka in Matlab orodja Annotated Web Ears (AWE)

Opis v angleščini: Annotated Web Ears (AWE) is a dataset of ear images gathered from the web and in the current form contains 1000 ear images of 100 distinct subjects. The dataset was collected for the goal of studying unconstrained ear recognition and is made publicly available to the community. The dataset comes with a Matlab toolbox dedicated to research in ear recognition. The AWE toolbox implements several state-of-the-art ear recognition techniques and allows for rapid experimentation with the AWE dataset.
Dosegljivo preko: AWE homepage
Opis: PDF
Podatkovna zbirka Extended Annotated Web Ears (AWEx)
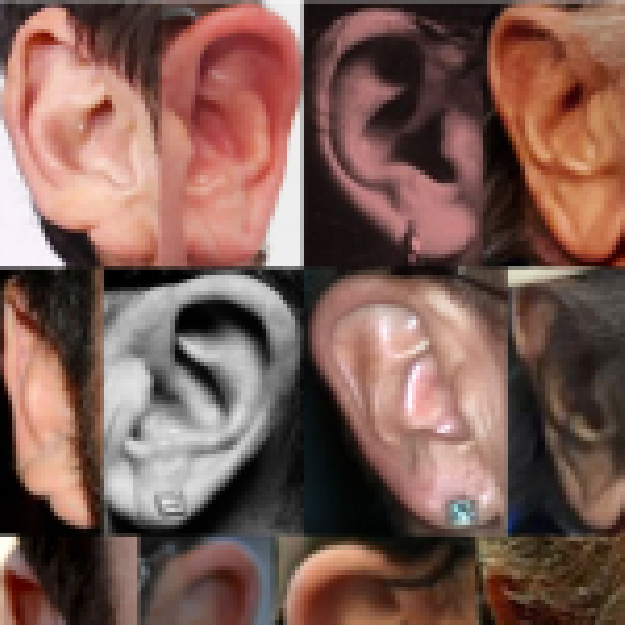
Opis v angleščini: AWEx is an extended version of the AWE dataset and contains ear images of more than 330 subjects. The dataset is available upon request. For contact information follow the AWE homepage link.
Dosegljivo preko: AWE homepage
Opis: PDF
Podatkovna zbirka Annotated Web Ears for segmentation AWE Dataset4Seg

Opis v angleščini: This version of the AWE dataset contains 1.000 images of 100 persons with the pixel-wise annotations of ear locations. The dataset is available upon request. For contact information follow the AWE homepage link.
Dosegljivo preko: AWE homepage
Opis: PDF
Podatkovna zbirka Sclera Blood Vessels, Periocular and Iris (SBVPI)
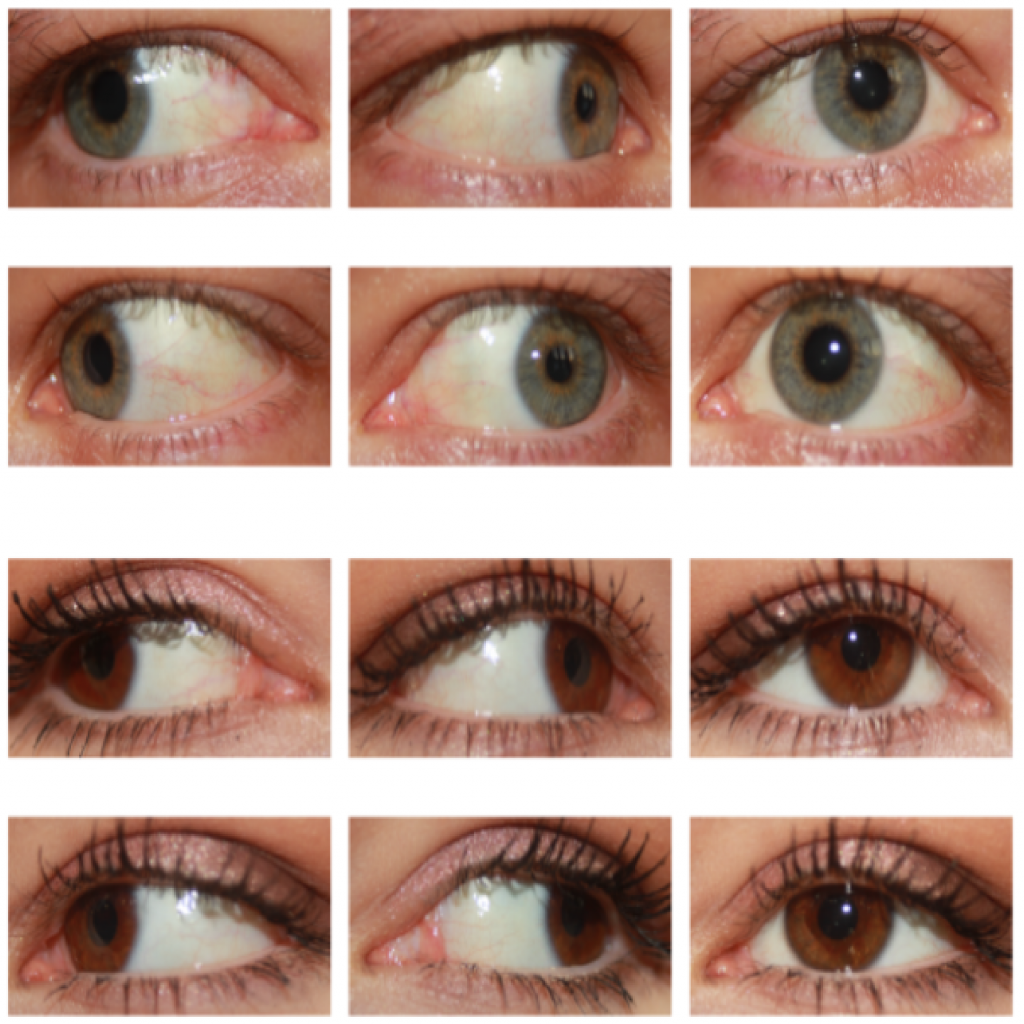
Opis v angleščini: SBVPI (Sclera Blood Vessels, Periocular and Iris) is a publicly available dataset primarily intended for sclera and periocular recognition research. It was developed at the Faculty of Computer and Information Science, University of Ljubljana in 2018. It consists of 2399 high quality eye images (3000 x 1700 pixels) belonging to 55 different identities. For each identity at least 32 images with 4 different look directions (straight, left, right, up) are available. Each image is annotated with an ID, gender, eye (left/right), view direction and sample number labels. Unlike other similar datasets, it includes corresponding per-pixels annotations of sclera, sclera vascular structures, iris, pupil and periocular region
Dosegljivo preko: SBVPI homepage
Članek: Segmentation and Recovery of Superquadric Models using Convolutional Neural Networks
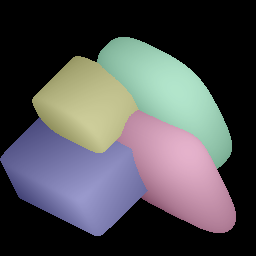
Opis v angleščini: In this paper we address the problem of representing 3D visual data with parameterized volumetric shape primitives. Specifically, we present a (two-stage) approach built around convolutional neural networks (CNNs) capable of segmenting complex depth scenes into the simpler geometric structures that can be represented with superquadric models. In the first stage, our approach uses a Mask-RCNN model to identify superquadric-like structures in depth scenes and then fits superquadric models to the segmented structures using a specially designed CNN regressor. Using our approach we are able to describe complex structures with a small number of interpretable parameters. We evaluated the proposed approach on synthetic as well as real-world depth data and show that our solution does not only result in competitive performance in comparison to the state-of-the-art, but is able to decompose scenes into a number of superquadric models at a fraction of the time required by competing approaches. We make all data and models used in the paper available from https://lmi.fe.uni-lj.si/research/resources/sq-seg/.
Available from: LMI website
Opis: PDF